The Stages of Vulnerability Management
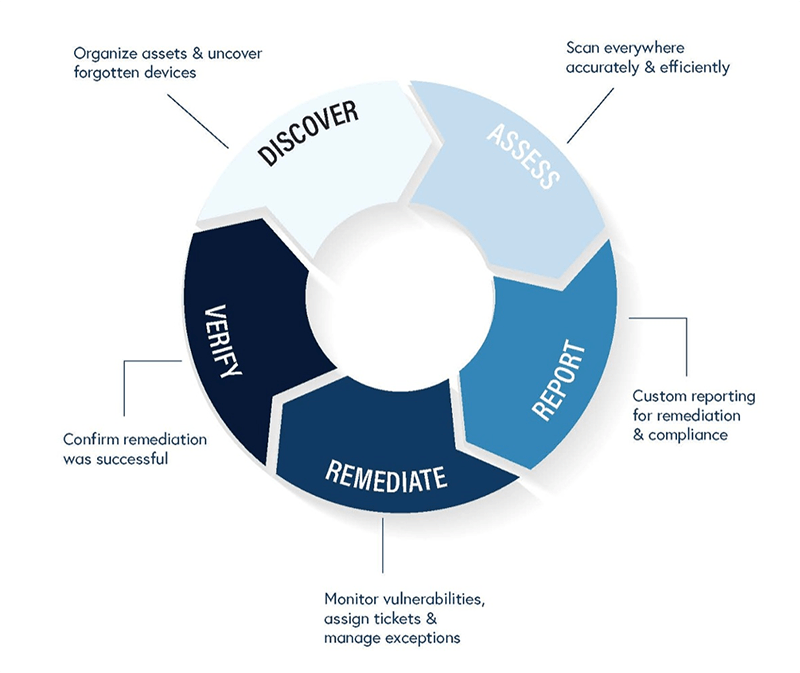
The typical vulnerability management process breaks down into multiple stages aimed at analyzing, prioritizing, and protecting your network.
Stage 1: Discover
The initial stage of the vulnerability management process is all about preparing for the vulnerability scans and tests and making sure your bases are covered. This means organizing all your company assets and uncovering any forgotten devices.
Compile all of the assets you need to test, determine their importance and who can access them (whether just administrators or your whole team). Work to maintain a continuously updated inventory so you can provide a map of the vulnerabilities throughout your network.
Stage 2: Assess
Once you’ve compiled all of your devices and inventory, the next stage involves the tests to make sure every device is scanned, both accurately and efficiently.
It’s not just about knowing the vulnerabilities, but gaining timely, efficient access to the information. If you aren’t receiving the data from a credible source, you might be wasting your time on false positives.
Once you’re aware of the potential risks on your devices, the next step is to prioritize those vulnerabilities. With the large number of vulnerabilities disclosed every day, it can seem impossible to manage them all, making it all the more significant to prioritize the biggest risks and resolve those first.
Stage 3: Report
All this data is then compiled into a custom report, giving details on the vulnerabilities and how to prioritize them. These reports will include recommendations as well as the best plan to triage the risks quickly and seamlessly.
It should include the actions to take and give step-by-step instructions to fix the problem. The purpose of the report is to significantly decrease the security risk that these vulnerabilities present in a practical way.
Stage 4: Remediate
In the stage of remediation, the goal is to monitor vulnerabilities, assign tickets, and manage exceptions.
As vulnerabilities are detected and reported, the next step in the vulnerability management process is to correct, monitor, or remove those vulnerabilities. This can be accomplished through the necessary updates and patches or workarounds to avoid the threat.
This stage is then repeated as new vulnerabilities are discovered. The network and its devices need to be continuously monitored to detect and find new vulnerabilities that might lead to potential, future threats.
Stage 5: Verify
The final step is to verify the success of the entire process. This step not only helps you see that the mitigation was successful but also maintains transparency and accountability across the company. The whole goal is to reduce the attack surface of a company, findings ways to minimize the threat of an attack by decreasing vulnerabilities.
With an ever-growing number of vulnerabilities, it’s challenging to know how to detect them on your own, let alone prioritize and remediate them. Equip your team to fight back by investing in a vulnerability management tool and team to minimize the risk and potential threats.
https://blog.teamascend.com/stages-of-vulnerability-management
20 Vulnerability Management Interview Questions and Answers
Prepare for the types of questions you are likely to be asked when interviewing for a position where Vulnerability Management will be used.
Vulnerability management is the process of identifying, classifying, remediating, and mitigating vulnerabilities. It is a critical part of an organization’s security program and is important for any organization that wants to protect its systems and data.
When interviewing for a position in vulnerability management, it is important to be prepared to answer questions about your experience and knowledge. In this article, we review some of the most common questions you may be asked during a job interview for a vulnerability management position.
Vulnerability Management Interview Questions and Answers
Here are 20 commonly asked Vulnerability Management interview questions and answers to prepare you for your interview:
1. What is vulnerability management?
Vulnerability management is the process of identifying, classifying, remediating, and mitigating vulnerabilities. This can be done through a variety of means, such as vulnerability assessments, which can be either manual or automated. Vulnerability management is important in order to keep systems and networks secure, as well as to ensure compliance with industry and government regulations.
2. Can you explain the difference between a risk and a vulnerability?
A risk is a potential for harm that could occur if a particular threat is realized. A vulnerability is a weakness or flaw in a system that could be exploited by a threat.
3. How can one assess vulnerabilities in an organization?
There are a few ways to assess vulnerabilities in an organization. One way is to use a vulnerability scanner, which is a tool that can scan systems and networks for known vulnerabilities. Another way is to manually assess systems and networks for vulnerabilities. This can be done by looking for common security issues, such as weak passwords or unpatched software.
4. What are some of the most common tools used for vulnerability scanning?
Some of the most common tools used for vulnerability scanning are NMAP, Nessus, and OpenVAS.
5. What do you understand by CVSS scores?
CVSS scores are a measure of the potential severity of a given vulnerability. They are calculated using a number of factors, including the nature of the vulnerability, the ease of exploitation, and the potential impact of exploitation. The scores range from 0 to 10, with 10 being the most severe.
6. How does asset classification help with vulnerability management?
Asset classification is the process of identifying and categorizing assets based on their value to the organization. This helps with vulnerability management because it allows the organization to prioritize which assets to protect first, and which assets can be left more vulnerable. For example, an organization might classify its assets as follows:
– Critical: Assets that are essential to the operation of the organization and cannot be replaced
– Important: Assets that are important to the operation of the organization but can be replaced
– Less Important: Assets that are not essential to the operation of the organization and can be replaced
By classifying its assets, the organization can then prioritize its vulnerability management efforts accordingly.
7. What’s the difference between false positives, false negatives, and true positives?
A false positive is when a vulnerability is reported that doesn’t actually exist. A false negative is when a vulnerability is not reported but does exist. A true positive is when a vulnerability is reported and does exist.
8. Are there any standard metrics that can be used to measure the effectiveness of a vulnerability management program?
There are a few standard metrics that can be used to measure the effectiveness of a vulnerability management program. These include the number of vulnerabilities that are found and remediated, the time it takes to find and remediate vulnerabilities, and the number of false positives that are generated.
9. What are the key steps involved in developing a vulnerability management process?
The key steps involved in developing a vulnerability management process are:
1. Identifying vulnerabilities: This step involves identifying potential security risks and weaknesses in systems and applications.
2. Assessing vulnerabilities: This step involves assessing the severity of each identified vulnerability and determining the best way to mitigate or eliminate it.
3. Mitigating vulnerabilities: This step involves taking steps to reduce the risk posed by each identified vulnerability, such as patching or upgrading software.
4. Monitoring vulnerabilities: This step involves continuously monitoring systems and applications for new or changed vulnerabilities.
10. Why do you think it’s important to create a patching policy?
A patching policy is important because it provides a consistent and reliable method for keeping systems up-to-date and secure. By having a patching policy in place, you can ensure that all systems are patched in a timely manner and that no critical security vulnerabilities are left unaddressed.
11. How would you approach determining which vulnerabilities should be fixed first in a system?
In order to determine which vulnerabilities should be fixed first in a system, you would need to prioritize them based on the severity of the issue and the likelihood of exploitation. The most severe vulnerabilities should be fixed first, as they pose the greatest risk to the system. However, you also need to take into account the likelihood of exploitation, as vulnerabilities that are more likely to be exploited pose a greater risk as well.
12. Where should all data related to vulnerability assessment be stored?
All data related to vulnerability assessment should be stored in a central location, such as a vulnerability management system. This will allow for easy access and analysis of the data, as well as providing a way to track and trend vulnerabilities over time.
13. What are the different types of hackers? Do you know how they differ from each other?
There are three main types of hackers: black hat, white hat, and gray hat. Black hat hackers are the ones you typically think of when you hear the word “hacker.” They are the ones who break into systems for malicious purposes, such as stealing data or causing damage. White hat hackers are the good guys. They use their hacking skills to help organizations improve their security by finding and fixing vulnerabilities. Gray hat hackers are somewhere in between. They may sometimes act without permission, but their motives are usually not malicious.
14. What do you understand about information security?
Information security is the practice of protecting electronic information by mitigating information risks and vulnerabilities. Information risks can include unauthorized access, use, disclosure, interception, or destruction of data. Data can include, but is not limited to, the confidential information of business or individual users.
15. What is the difference between cyber warfare and cyber terrorism?
Cyber warfare is typically conducted by nation-states against other nation-states, with the aim of disrupting, disabling, or destroying critical infrastructure or military targets. Cyber terrorism, on the other hand, is typically carried out by non-state actors with the aim of causing terror or panic among a civilian population.
16. What is your understanding of threat modeling?
Threat modeling is the process of identifying potential security threats and vulnerabilities in a system and then designing countermeasures to mitigate those risks. It is an important part of any security strategy and can help organizations to proactively protect their systems and data.
17. In what ways can digital certificates be compromised?
One way digital certificates can be compromised is if the private key is stolen. If the private key is stolen, then an attacker can use it to sign malicious code and impersonate the owner of the certificate. Another way digital certificates can be compromised is if the certificate authority’s database is hacked. If the database is hacked, then an attacker can issue themselves a valid certificate.
18. What is Common Vulnerability Scoring System? How does it work?
The Common Vulnerability Scoring System (CVSS) is a framework for rating the severity of computer system security vulnerabilities. CVSS assigns a numeric score to each vulnerability, which is then used to determine the overall risk posed by the vulnerability. The score is based on a number of factors, including the nature of the vulnerability, the potential impact of the vulnerability, and the likelihood of the vulnerability being exploited.
19. What is your understanding of the Pareto principle as applied to IT Security?
The Pareto principle, also known as the 80/20 rule, states that 80% of the effects come from 20% of the causes. In the context of IT security, this means that 80% of the security risks come from 20% of the vulnerabilities. Therefore, it is important to focus on identifying and addressing the most common and severe vulnerabilities in order to have the biggest impact on overall security.
20. Name three categories of security breaches
1. Malicious attacks: These are intentional attacks carried out by individuals or groups with the aim of causing harm or stealing data.
2. Accidental breaches: These can occur when employees make mistakes or when systems are not properly configured.
3. Third-party breaches: These happen when a third party that has access to your systems, such as a contractor or vendor, suffers a breach

