Windows Sever 2008/R2 Interview questions Part 1
Difference between 2003 and 2008
1) 2008 is combination of vista and windows 2003r2. Some new services are introduced in it
1. RODC one new domain controller introduced in it [Read-only Domain controllers.]
2. WDS (windows deployment services) instead of RIS in 2003 server
3. shadow copy for each and every folders
4.boot sequence is changed
5.installation is 32 bit where as 2003 it is 16 as well as 32 bit, that’s why installation of 2008 is faster
6.services are known as role in it
7. Group policy editor is a separate option in ads
1. RODC one new domain controller introduced in it [Read-only Domain controllers.]
2. WDS (windows deployment services) instead of RIS in 2003 server
3. shadow copy for each and every folders
4.boot sequence is changed
5.installation is 32 bit where as 2003 it is 16 as well as 32 bit, that’s why installation of 2008 is faster
6.services are known as role in it
7. Group policy editor is a separate option in ads
2) The main difference between 2003 and 2008 is Virtualization, management.
2008 has more inbuilt components and updated third party drivers Microsoft introduces new feature with 2k8 that is Hyper-V Windows Server 2008 introduces Hyper-V (V for Virtualization) but only on 64bit versions. More and more companies are seeing this as a way of reducing hardware costs by running several ‘virtual’ servers on one physical machine. If you like this exciting technology, make sure that you buy an edition of Windows Server 2008 that includes Hyper-V, then launch the Server Manger, add Roles.
2008 has more inbuilt components and updated third party drivers Microsoft introduces new feature with 2k8 that is Hyper-V Windows Server 2008 introduces Hyper-V (V for Virtualization) but only on 64bit versions. More and more companies are seeing this as a way of reducing hardware costs by running several ‘virtual’ servers on one physical machine. If you like this exciting technology, make sure that you buy an edition of Windows Server 2008 that includes Hyper-V, then launch the Server Manger, add Roles.
Windows server 2008 new features
1. Virtualization with Hyper V
2. Server Core – provides the minimum installation
required to carry out a specific server role, such as for a DHCP, DNS or
print server. From a security standpoint, this is attractive. Fewer
applications and services on the sever make for a smaller attack
surface. In theory, there should also be less maintenance and management
with fewer patches to install, and the whole server could take up as
little as 3Gb of disk space according to Microsoft
3. IIS 7
4. Role based installation – rather than configuring a
full server install for a particular role by uninstalling unnecessary
components (and installing needed extras), you simply specify the role
the server is to play, and Windows will install what’s necessary —
nothing more.
5. Read Only Domain Controllers (RODC)
It’s hardly news that branch offices often lack skilled IT staff to administer their servers, but they also face another, less talked about problem. While corporate data centers are often physically secured, servers at branch offices rarely have the same physical security protecting them. This makes them a convenient launch pad for attacks back to the main corporate servers. RODC provides a way to make an Active Directory database read-only. Thus, any mischief carried out at the branch office cannot propagate its way back to poison the Active Directory system as a whole. It also reduces traffic on WAN links.
It’s hardly news that branch offices often lack skilled IT staff to administer their servers, but they also face another, less talked about problem. While corporate data centers are often physically secured, servers at branch offices rarely have the same physical security protecting them. This makes them a convenient launch pad for attacks back to the main corporate servers. RODC provides a way to make an Active Directory database read-only. Thus, any mischief carried out at the branch office cannot propagate its way back to poison the Active Directory system as a whole. It also reduces traffic on WAN links.
6. Enhanced terminal services
Terminal services has been beefed up in Server 2008 in a number of ways. TS RemoteApp enables remote users to access a centralized application (rather than an entire desktop) that appears to be running on the local computer’s hard drive. These apps can be accessed via a Web portal or directly by double-clicking on a correctly configured icon on the local machine. TS Gateway secures sessions, which are then tunnelled over https, so users don’t need to use a VPN to use RemoteApps securely over the Internet. Local printing has also been made significantly easier.
Terminal services has been beefed up in Server 2008 in a number of ways. TS RemoteApp enables remote users to access a centralized application (rather than an entire desktop) that appears to be running on the local computer’s hard drive. These apps can be accessed via a Web portal or directly by double-clicking on a correctly configured icon on the local machine. TS Gateway secures sessions, which are then tunnelled over https, so users don’t need to use a VPN to use RemoteApps securely over the Internet. Local printing has also been made significantly easier.
7. Network Access Protection
Microsoft’s system for ensuring that clients connecting to Server 2008 are patched, running a firewall and in compliance with corporate security policies — and that those that are not can be remediated — is useful. However, similar functionality has been and remains available from third parties.
Microsoft’s system for ensuring that clients connecting to Server 2008 are patched, running a firewall and in compliance with corporate security policies — and that those that are not can be remediated — is useful. However, similar functionality has been and remains available from third parties.
8. Windows PowerShell
Microsoft’s new (ish) command line shell and scripting language has
proved popular with some server administrators, especially those used to
working in Linux environments. Included in Server 2008, PowerShell can
make some jobs quicker and easier to perform than going through the GUI.
Although it might seem like a step backward in terms of user friendly
operation, it’s one of those features that once you’ve gotten used to
it; you’ll never want to give up.
Restartable Active Directory Domain Services: You can
now perform many actions, such as offline defragmentation of the
database, simply by stopping Active Directory. This reduces the number
of instances in which you must restart the server in Directory Services
Restore Mode and thereby reduces the length of time the domain
controller is unavailable to serve requests from
Enhancements to Group Policy: Microsoft has added many
new policy settings. In particular, these settings enhance the
management of Windows Vista client computers. All policy management is
now handled by means of the Group Policy Management Console (GPMC),
which was an optional feature first added to Windows Server 2003 R2. In
addition, Microsoft has added new auditing capabilities to Group Policy
and added a searchable database for locating policy settings from within
GPMC. In Windows Server 2008 R2, GPMC enables you to use a series of
PowerShell cmdlets to automate many of the tasks (such as maintenance
and linking of GPOs) that you would otherwise perform in the GUI. In
addition, R2 adds new policy settings that enhance the management of
Windows 7 computers.
Windows Server 2008 R2 new features:
Active Directory Recycle Bin
Windows PowerShell 2.0
Active Directory Administrative Center (ADAC)
Offline domain join
Active Directory health check
Active Directory Web Services
Active Directory Management Pack
Windows Server Migration Tools
Managed Service Accounts
What is server core? How do you configure and manage a windows server 2008 core installation?
The Server Core installation option is an option that you can use for
installing Windows Server 2008 or Windows Server 2008 R2. A Server Core
installation provides a minimal environment for running specific server
roles, which reduces the maintenance and management requirements and the
attack surface for those server roles. A server running a Server Core
installation of Windows Server 2008 supports the following server roles:
- Active Directory Domain Services (AD DS)
- Active Directory Lightweight Directory Services (AD LDS)
- DHCP Server
- DNS Server
- File Services
- Hyper-V
- Print Services
- Streaming Media Services
- Web Server (IIS)
A server running a Server Core installation of Windows Server 2008 R2 supports the following server roles:
- Active Directory Certificate Services
- Active Directory Domain Services
- Active Directory Lightweight Directory Services (AD LDS)
- DHCP Server
- DNS Server
- File Services (including File Server Resource Manager)
- Hyper-V
- Print and Document Services
- Streaming Media Services
- Web Server (including a subset of ASP.NET)
A Server Core installation does not include the traditional full
graphical user interface. Once you have configured the server, you can
manage it locally at a command prompt or remotely using a Terminal
Server connection. You can also manage the server remotely using the
Microsoft Management Console (MMC) or command-line tools that support
remote use.
Benefits of a Server Core installation
The Server Core installation option of Windows Server 2008 or Windows Server 2008 R2 provides the following benefits:
- Reduced maintenance. Because the Server Core installation option installs only what is required to have a manageable server for the supported roles, less maintenance is required than on a full installation of Windows Server 2008.
- Reduced attack surface. Because Server Core installations are minimal, there are fewer applications running on the server, which decreases the attack surface.
- Reduced management. Because fewer applications and services are installed on a server running the Server Core installation, there is less to manage.
- Less disk space required. A Server Core installation requires only about 3.5 gigabytes (GB) of disk space to install and approximately 3 GB for operations after the installation.
How do you promote a Server Core to DC?
In order to install Active Directory DS on your server core machine you will need to perform the following tasks:
1. Configure an unattend text file,
containing the instructions for the DCPROMO process. In this example you
will create an additional DC for a domain called petrilab.local:
2. Configure the right server core settings
After that you need to make sure the core machine is properly configured.
- Perform any configuration setting that you require (tasks such as changing computer name, changing and configure IP address, subnet mask, default gateway, DNS address, firewall settings, configuring remote desktop and so on).
- After changing the required server configuration, make sure that for the task of creating it as a DC – you have the following requirements in place:
- A partition formatted with NTFS (you should, it’s a server…)
- A network interface card, configure properly with the right driver
- A network cable plugged in
- The right IP address, subnet mask, default gateway
And most importantly, do not forget:
- The right DNS setting, in most cases, pointing to an existing internal DNS in your corporate network
3. Copy the unattend file to the server core machine
Now you need to copy the unattend file from wherever you’ve stored it.
You can run it from a network location but I prefer to have it locally
on the core machine. You can use the NET USE command on server core to
map to a network path and copy the file to the local drive. You can also
use a regular server/workstation to graphically access the core’s C$
drive (for example) and copy the file to that location.
4. Run the DCPROMO process
Next you need to manually run DCPROMO. To run the Active Directory
Domain Services Installation Wizard in unattended mode, use the
following command at a command prompt:
Dcpromo /unattend
Reboot the machine
In order to reboot the server core machine type the following text in the command prompt and press Enter.
shutdown /r /t 0
What are RODCs? What are advantages?
A read-only domain controller (RODC) is a new type of domain controller
in the Windows Server® 2008 operating system. With an RODC,
organizations can easily deploy a domain controller in locations where
physical security cannot be guaranteed. An RODC hosts read-only
partitions of the Active Directory Domain Services (AD DS) database.
Before the release of Windows Server 2008, if users had to authenticate
with a domain controller over a wide area network (WAN), there was no
real alternative. In many cases, this was not an efficient solution.
Branch offices often cannot provide the adequate physical security that
is required for a writable domain controller. Furthermore, branch
offices often have poor network bandwidth when they are connected to a
hub site. This can increase the amount of time that is required to log
on. It can also hamper access to network resources.
Beginning with Windows Server 2008, an organization can deploy an RODC
to address these problems. As a result, users in this situation can
receive the following benefits:
- Improved security
- Faster logon times
- More efficient access to resources on the network
What does an RODC do?
Inadequate physical security is the most common reason to consider
deploying an RODC. An RODC provides a way to deploy a domain controller
more securely in locations that require fast and reliable authentication
services but cannot ensure physical security for a writable domain
controller.
However, your organization may also choose to deploy an RODC for special
administrative requirements. For example, a line-of-business (LOB)
application may run successfully only if it is installed on a domain
controller. Or, the domain controller might be the only server in the
branch office, and it may have to host server applications.
In such cases, the LOB application owner must often log on to the domain
controller interactively or use Terminal Services to configure and
manage the application. This situation creates a security risk that may
be unacceptable on a writable domain controller.
An RODC provides a more secure mechanism for deploying a domain
controller in this scenario. You can grant a non administrative domain
user the right to log on to an RODC while minimizing the security risk
to the Active Directory forest.
You might also deploy an RODC in other scenarios where local storage of
all domain user passwords is a primary threat, for example, in an
extranet or application-facing role.
How do you install an RODC?
1 Make sure you are a member of Domain Admin group
2. Ensure that the forest functional level is Windows Server 2003 or higher
3. Run adprep /rodcprep
3. Install a writable domain controller that runs Windows Server 2008 –
An RODC must replicate domain updates from a writable domain controller
that runs Windows Server 2008. Before you install an RODC, be sure to
install a writable domain controller that runs Windows Server 2008 in
the same domain. The domain controller can run either a full
installation or a Server Core installation of Windows Server 2008. In
Windows Server 2008, the writable domain controller does not have to
hold the primary domain controller (PDC) emulator operations master
role.
4. You can install an RODC on either a full installation of Windows
Server 2008 or on a Server Core installation of Windows Server 2008.
Follow the below steps:
- Click Start, type dcpromo, and then press ENTER to start the Active Directory Domain Services Installation Wizard.
- On the Choose a Deployment Configuration page, click Existing forest, click Add a domain controller to an existing domain
- On the Network Credentials page, type the name of a domain in the forest where you plan to install the RODC. If necessary, also type a user name and password for a member of the Domain Admins group, and then clickNext.
- Select the domain for the RODC, and then click Next.
- Click the Active Directory site for the RODC and click next
- Select the Read-only domain controller check box, as shown in the following illustration. By default, the DNS server check box is also selected. To run the DNS server on the RODC, another domain controller running Windows Server 2008 must be running in the domain and hosting the DNS domain zone. An Active Directory–integrated zone on an RODC is always a read-only copy of the zone file. Updates are sent to a DNS server in a hub site instead of being made locally on the RODC.
- To use the default folders that are specified for the Active Directory database, the log files, and SYSVOL, clickNext.
- Type and then confirm a Directory Services Restore Mode password, and then click Next.
- Confirm the information that appears on the Summary page, and then click Next to start the AD DS installation. You can select the Reboot on completion check box to make the rest of the installation complete automatically.
What is the minimum requirement to install Windows 2008 server?
Talk about all the AD-related roles in Windows Server 2008/R2.
Active Directory Domain Services
Active Directory Domain Services (AD DS), formerly known as Active
Directory Directory Services, is the central location for configuration
information, authentication requests, and information about all of the
objects that are stored within your forest. Using Active Directory, you
can efficiently manage users, computers, groups, printers, applications,
and other directory-enabled objects from one secure, centralized
location.
Benefits
- Lower costs of managing Windows networks.
- Simplify identity management by providing a single view of all user information.
- Boost security with the ability to enable multiple types of security mechanisms within a single network.
- Improve compliance by using Active Directory as a primary source for audit data.
Active Directory Rights Management Services
Your organization’s intellectual property needs to be safe and highly
secure. Active Directory Rights Management Services, a component of
Windows Server 2008, is available to help make sure that only those
individuals who need to view a file can do so. AD RMS can protect a file
by identifying the rights that a user has to the file. Rights can be
configured to allow a user to open, modify, print, forward, or take
other actions with the rights-managed information. With AD RMS, you can
now safeguard data when it is distributed outside of your network.
Active Directory Federation Services
Active Directory Federation Services is a highly secure, highly
extensible, and Internet-scalable identity access solution that allows
organizations to authenticate users from partner organizations. Using AD
FS in Windows Server 2008, you can simply and very securely grant
external users access to your organization’s domain resources. AD FS can
also simplify integration between untrusted resources and domain
resources within your own organization.
Active Directory Certificate Services
Most organizations use certificates to prove the identity of users or
computers, as well as to encrypt data during transmission across
unsecured network connections. Active Directory Certificate Services (AD
CS) enhances security by binding the identity of a person, device, or
service to their own private key. Storing the certificate and private
key within Active Directory helps securely protect the identity, and
Active Directory becomes the centralized location for retrieving the
appropriate information when an application places a request.
Active Directory Lightweight Directory Services
Active Directory Lightweight Directory Service (AD LDS), formerly known
as Active Directory Application Mode, can be used to provide directory
services for directory-enabled applications. Instead of using your
organization’s AD DS database to store the directory-enabled application
data, AD LDS can be used to store the data. AD LDS can be used in
conjunction with AD DS so that you can have a central location for
security accounts (AD DS) and another location to support the
application configuration and directory data (AD LDS). Using AD LDS, you
can reduce the overhead associated with Active Directory replication,
you do not have to extend the Active Directory schema to support the
application, and you can partition the directory structure so that the
AD LDS service is only deployed to the servers that need to support the
directory-enabled application.
What are the new Domain and Forest Functional Levels in Windows Server 2008/R2?
Domain Function Levels
To activate a new domain function level, all DCs in the domain must be
running the right operating system. After this requirement is met, the
administrator can raise the domain functional level. Here’s a list of
the available domain function levels available in Windows Server 2008:
Windows 2000 Native Mode
This is the default function level for new Windows Server 2008 Active Directory domains.
Supported Domain controllers – Windows 2000, Windows Server 2003, Windows Server 2008.
Windows Server 2003 Mode
To activate the new domain features, all domain controllers in the
domain must be running Windows Server 2003. After this requirement is
met, the administrator can raise the domain functional level to Windows
Server 2003.
Supported Domain controllers – Windows Server 2003, Windows Server 2008.
Windows Server 2008 Mode
Supported Domain controllers – Windows Server 2008.
Windows 2008 Forest function levels
Forest functionality activates features across all the domains in your
forest. To activate a new forest function level, all the domain in the
forest must be running the right operating system and be set to the
right domain function level. After this requirement is met, the
administrator can raise the forest functional level. Here’s a list of
the available forest function levels available in Windows Server 2008:
Windows 2000 forest function level
This is the default setting for new Windows Server 2008 Active Directory forests.
Supported Domain controllers in all domains in the forest – Windows 2000, Windows Server 2003, Windows Server 2008.
Windows Server 2003 forest function level
To activate new forest-wide features, all domain controllers in the forest must be running Windows Server 2003.
Supported Domain controllers in all domains in the forest – Windows Server 2003, Windows Server 2008.
Windows Server 2008 forest function level
To activate new forest-wide features, all domain controllers in the forest must be running Windows Server 2008.
Supported Domain controllers in all domains in the forest – Windows Server 2008.
To activate the new domain features, all domain controllers in the
domain must be running Windows Server 2008. After this requirement is
met, the administrator can raise the domain functional level to Windows
Server 2008.
When a child domain is created in
the domain tree, what type of trust relationship exists between the new
child domain and the trees root domain?
Transitive and two way.
Which Windows Server 2008 tools make it easy to manage and configure a servers roles and features?
The Server Manager window enables you to view the roles and features
installed on a server and also to quickly access the tools used to
manage these various roles and features. The Server Manager can be used
to add and remove roles and features as needed
What is WDS? How is WDS configured and managed on a server running Windows Server 2008?
The Windows Deployment Services is the updated and redesigned version of
Remote Installation Services (RIS). Windows Deployment Services enables
you to deploy Windows operating systems, particularly Windows Vista.
You can use it to set up new computers by using a network-based
installation. This means that you do not have to install each operating
system directly from a CD or DVD.
Benefits of Windows Deployment Services
Windows Deployment Services provides organizations with the following benefits:
- Allows network-based installation of Windows operating systems, which reduces the complexity and cost when compared to manual installations.
- Deploys Windows images to computers without operating systems.
- Supports mixed environments that include Windows Vista, Microsoft Windows XP and Microsoft Windows Server 2003.
- Built on standard Windows Vista setup technologies including Windows PE, .wim files, and image-based setup.
Prerequisites for installing Windows Deployment Services
Your computing environment must meet the following technical requirements to install Windows Deployment Services:
- Active Directory. A Windows Deployment Services server must be either a member of an Active Directory domain or a domain controller for an Active Directory domain. The Active Directory domain and forest versions are irrelevant; all domain and forest configurations support Windows Deployment Services.
- DHCP. You must have a working Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) server with an active scope on the network because Windows Deployment Services uses PXE, which relies on DHCP for IP addressing.
- DNS. You must have a working Dynamic Name Services (DNS) server on the network to run Windows Deployment Services.
- An NTFS partition. The server running Windows Deployment Services requires an NTFS file system volume for the image store.
- Credentials. To install the role, you must be a member of the Local Administrators group on the Windows Deployment Services server. To install an image, you must be a member of the Domain Users group.
- Windows Server 2003 SP1 or SP2 with RIS installed. RIS does not have to be configured, but must be installed.
Name some of the major changes in GPO in Windows Server 2008.
Cost savings through power options
In Windows Server 2008, all power options have been Group Policy
enabled, providing a potentially significant cost savings. Controlling
power options through Group Policy could save organizations a
significant amount of money. You can modify specific power options
through individual Group Policy settings or build a custom power plan
that is deployable by using Group Policy.
Ability to block device installation
In Windows Server 2008, you can centrally restrict devices from being
installed on computers in your organization. You will now be able to
create policy settings to control access to devices such as USB drives,
CD-RW drives, DVD-RW drives, and other removable media.
Improved security settings
In Windows Server 2008, the firewall and IPsec Group Policy settings are
combined to allow you to leverage the advantages of both technologies,
while eliminating the need to create and maintain duplicate
functionality. Some scenarios supported by these combined firewall and
IPsec policy settings are secure server-to-server communications over
the Internet, limiting access to domain resources based on trust
relationships or health of a computer, and protecting data communication
to a specific server to meet regulatory requirements for data privacy
and security.
Expanded Internet Explorer settings management
In Windows Server 2008, you can open and edit Internet Explorer Group
Policy settings without the risk of inadvertently altering the state of
the policy setting based on the configuration of the administrative
workstation. This change replaces earlier behavior in which some
Internet Explorer policy settings would change based on the policy
settings enabled on the administrative workstation used to view the
settings
Printer assignment based on location
The ability to assign printers based on location in the organization or a
geographic location is a new feature in Windows Server 2008. In Windows
Server 2008, you can assign printers based on site location. When
mobile users move to a different location, Group Policy can update their
printers for the new location. Mobile users returning to their primary
locations see their usual default printers.
Printer driver installation delegated to users
In Windows Server 2008, administrators can now delegate to users the
ability to install printer drivers by using Group Policy. This feature
helps to maintain security by limiting distribution of administrative
credentials.
What is the AD Recycle Bin? How do you use it?
Active Directory Recycle Bin helps minimize directory service downtime
by enhancing your ability to preserve and restore accidentally deleted
Active Directory objects without restoring Active Directory data from
backups, restarting Active Directory Domain Services (AD DS), or
rebooting domain controllers.
When you enable Active Directory Recycle Bin, all link-valued and
non-link-valued attributes of the deleted Active Directory objects are
preserved and the objects are restored in their entirety to the same
consistent logical state that they were in immediately before deletion.
For example, restored user accounts automatically regain all group
memberships and corresponding access rights that they had immediately
before deletion, within and across domains.
Active Directory Recycle Bin is functional for both AD DS and
Active Directory Lightweight Directory Services (AD LDS) environments.
By default, Active Directory Recycle Bin in Windows Server 2008 R2 is
disabled. To enable it, you must first raise the forest functional level
of your AD DS or AD LDS environment to Windows Server 2008 R2, which in
turn requires all forest domain controllers or all servers that host
instances of AD LDS configuration sets to be running Windows
Server 2008 R2.
To enable Active Directory Recycle Bin using the Enable-ADOptionalFeature cmdlet
1. Click Start, click Administrative Tools, right-click Active Directory Module for Windows PowerShell, and then click Run as administrator.
- At the Active Directory module for Windows PowerShell command prompt, type the following command, and then press ENTER:
Enable-ADOptionalFeature -Identity -Scope -Target
For example, to enable Active Directory Recycle Bin for contoso.com, type the following command, and then press ENTER:
Enable-ADOptionalFeature –Identity ‘CN=Recycle Bin Feature,CN=Optional
Features,CN=Directory Service,CN=Windows
NT,CN=Services,CN=Configuration,DC=contoso,DC=com’ –Scope
ForestOrConfigurationSet –Target ‘contoso.com’
What are AD Snapshots? How do you use them?
A snapshot is a shadow copy—created by the Volume Shadow Copy Service
(VSS)—of the volumes that contain the Active Directory database and log
files. With Active Directory snapshots, you can view the data inside
such a snapshot on a domain controller without the need to start the
server in Directory Services Restore Mode.
Windows Server 2008 has a new feature allowing administrators to create
snapshots of the Active Directory database for offline use. With AD
snapshots you can mount a backup of AD DS under a different set of ports
and have read-only access to your backups through LDAP.
There are quite a few scenarios for using AD snapshots. For example, if
someone has changed properties of AD objects and you need to revert to
their previous values, you can mount a copy of a previous snapshot to an
alternate port and easily export the required attributes for every
object that was changed. These values can then be imported into the
running instance of AD DS. You can also restore deleted objects or
simply view objects for diagnostic purposes.
It does not allow you to move or copy items or information from the
snapshot to the live database. In order to do that you will need to
manually export the relevant objects or attributes from the snapshot,
and manually import them back to the live AD database.
Steps for using Snapshot:
1. Create a snapshot:
open CMD.exe, Ntdsutil, activate instance ntds, snapshot, create, list all.
2. Mounting an Active Directory snapshot:
Before connecting to the snapshot we need to mount it. By looking at the
results of the List All command in above step, identify the snapshot
that you wish to mount, and note the number next to it.
Type Ntdsutil, Snapshot, List all, Mount 2. The snapshot gets mounted to
c:\$SNAP_200901250030_VOLUMEC$. Now you can refer this path to see the
objects in these snapshots.
3. Connecting an Active Directory snapshot:
In order to connect to the AD snapshot you’ve mounted you will need to
use the DSAMAIN command. DSAMAIN is a command-line tool that is built
into Windows Server 2008. It is available if you have the Active
Directory Domain Services (AD DS) or Active Directory Lightweight
Directory Services (AD LDS) server role installed.
After using DSAMAIN to expose the information inside the AD snapshot,
you can use any GUI tool that can connect to the specified port, tools
such as Active Directory Users and Computers (DSA.msc), ADSIEDIT.msc, LDP.exe or
others. You can also connect to it by using command line tools such as
LDIFDE or CSVDE, tools that allow you to export information from that
database.
dsamain -dbpath ” c:\$SNAP_200901250030_VOLUMEC$\Windows\NTDS\ntds.dit” -ldapport 10289
The above command will allow you to access the database using port 10289.
Now you can useLDP.exetool to connect to this mounted instance.
4. Disconnecting from the Active Directory snapshot:
In order to disconnect from the AD snapshot all you need to do is to
type CTRL+C at the DSAMAIN command prompt window. You’ll get a message
indicating that the DS shut down successfully.
5. Unmounting the snapshot:
Run command, Ntdsutil, Snapshot, List all, Unmount 2.
What is Offline Domain Join? How do you use it?
You can use offline domain join to join computers to a
domain without contacting a domain controller over the network. You can
join computers to the domain when they first start up after an
operating system installation. No additional restart is necessary to
complete the domain join. This helps reduce the time and effort required
to complete a large-scale computer deployment in places such as
datacenters.
For example, an organization might need to deploy many virtual machines
within a datacenter. Offine domain join makes it possible for the
virtual machines to be joined to the domain when they initially start
following the operating system installation. No additional restart is
required to complete the domain join. This can significantly reduce the
overall time required for wide-scale virtual machine deployments.
A domain join establishes a trust relationship between a computer
running a Windows operating system and an Active Directory domain. This
operation requires state changes to AD DS and state changes on the
computer that is joining the domain. To complete a domain join in the
past using previous Windows operating systems, the computer that joined
the domain had to be running and it had to have network connectivity to
contact a domain controller. Offline domain join provides the following
advantages over the previous requirements:
- The Active Directory state changes are completed without any network traffic to the computer.
- The computer state changes are completed without any network traffic to a domain controller.
- Each set of changes can be completed at a different time.
What are Fine-Grained Passwords? How do you use them?
You can use fine-grained password policies to specify
multiple password policies within a single domain. You can use
fine-grained password policies to apply different restrictions for
password and account lockout policies to different sets of users in a
domain.
For example, you can apply stricter settings to privileged accounts and
less strict settings to the accounts of other users. In other cases, you
might want to apply a special password policy for accounts whose
passwords are synchronized with other data sources.
Talk about Restartable Active Directory Domain Services in Windows Server 2008/R2. What is this feature good for?
Restartable AD DS is a feature in Windows Server 2008 that you can use
to perform routine maintenance tasks on a domain controller, such as
applying updates or performing offline defragmentation, without
restarting the server.
While AD DS is running, a domain controller running Windows Server 2008
behaves the same way as a domain controller running
Microsoft® Windows® 2000 Server or Windows Server 2003.
While AD DS is stopped, you can continue to log on to the domain by
using a domain account if other domain controllers are available to
service the logon request. You can also log on to the domain with a
domain account while the domain controller is started in Directory
Services Restore Mode (DSRM) if other domain controllers are available
to service the logon request.
If no other domain controller is available, you can log on to the domain
controller where AD DS is stopped in Directory Services Restore Mode
(DSRM) only by using the DSRM Administrator account and password by
default, as in Windows 2000 Server Active Directory or
Windows Server 2003 Active Directory.
Benefits of restartable AD DS
Restartable AD DS reduces the time that is required to perform offline
operations such as offline defragmentation. It also improves the
availability of other services that run on a domain controller by
keeping them running when AD DS is stopped. In combination with the
Server Core installation option of Windows Server 2008, restartable
AD DS reduces the overall servicing requirements of a domain controller.
In Windows 2000 Server Active Directory and Windows Server 2003
Active Directory, you must restart the domain controller in DSRM when
you perform offline defragmentation of the database or apply security
updates. In contrast, you can stop Windows Server 2008 AD DS as you stop
other services that are running locally on the server. This makes it
possible to perform offline AD DS operations more quickly than you could
with Windows 2000 Server and Windows Server 2003.
You can use Microsoft Management Console (MMC) snap-ins, or the Net.exe command-line
tool, to stop or restart Active Directory® Domain Services (AD DS) in
the Windows Server® 2008 operating system. You can stop AD DS to perform
tasks, such as offline defragmentation of the AD DS database, without
restarting the domain controller. Other services that run on the server,
but that do not depend on AD DS to function, are available to service
client requests while AD DS is stopped. An example of such a service is
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP).
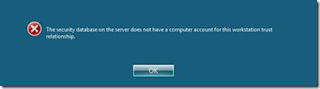
Before few days ago I returned snapshot/checkpoint with scvmm and turned on virtual machine, but when I tried to logon with domain user I gave this message, „The security database on the server does not have a computer account for this workstation trust relationship“. I need to mention that snapshot/checkpoint was old only three hours.
I logged in with local Administrator account and removed server from the
domain and again join to the domain. After restart I logged in with
domain account but few services didn’t start. I again restarted server,
tried to logon and I gave the same message „The security database on the server does not have a computer account for this workstation trust relationship“.
Solution/Workaround:
You need to do two things.
1. Reapply values in ADSI Edit (adsiedit.msc) or enter new if SPN missing.
Open adsiedit.msc like on picture below and check settings inservicePrincipalName
2. Restart the computer.
3. Login on to your server with local Administrator account.
4. Change domain from FQDN to the short name. In my case ekobit.corp change toekobit_corp
5. Restart your server and Login as the domain user.
Relax your mind and enjoy  .
.
NOTE: As you might know Winlogon service on Windows 7,
Windows Server 2008 and Windows Server 2008 R2 Operating Systems use
Kerberos logon. So the Service Principal Names (SPNs) need to be
configured properly to support Kerberos Authentication.
Other Reference Articles:
Kerberos Authentication Problems:http://blogs.technet.com/b/askds/archive/2008/05/29/kerberos-authentication-problems-service-principal-name-spn-issues-part-1.aspx
Symptoms when secure channel is broken:http://blogs.technet.com/b/asiasupp/archive/2007/01/18/typical-symptoms-when-secure-channel-is-broken.aspx
Machine Account Password Process:http://blogs.technet.com/b/askds/archive/2009/02/15/test2.aspx
Windows 2008 Server Interview Questions Part II
1. What are the Important Windows port numbers:
RDP – 3389 – (windows rdp port number and remote desktop port number)
FTP – 21 – (file transfer protocol)
TFTP – 69 – ( tftp port number )
Telnet – 23 – ( telnet port number)
SMTP – 25 – ( SMTP port number)
DNS – 53 – ( dns port number and Domain Name System port number)
DHCP – 68 – (DHCP port number and Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol port number )
POP3 – 110 – ( post office Protocol 3 port )
HTTP – 80 – (http port number)
HTTPS – 443 – (https port number)
NNTP – 119 – ( Network News Transfer Protocol Port number )
NTP – 123 – (ntp port number and network Time Protocol and SNTP port number )
IMAP – 143 – (Internet Message Access Protocol port number)
SSMTP – 465 – ( SMTP Over SSl )
SIMAP – 993 – ( IMAP Over SSL )
SPOP3 – 995 – ( POP# Over SS L)
Time – 123 – ( ntp port number and network Time Protocol and SNTP port number )
NetBios – 137 – ( Name Service )
NetBios – 139 – ( Datagram Service )
DHCP Client – 546 – (DHCP Client port number)
DHCP Server – 547 – (DHCP Server port number)
Global Catalog – 3268 – (Global Catalog port number)
LDAP – 389 – ( LDAP port number and Lightweight Directory Access Protocol port number )
RPC – 135 – (remote procedure call Port number)
Kerberos – 88 – ( Kerberos Port Number)
SSH – 22 – ( ssh port number and Secure Shell port number)
FTP – 21 – (file transfer protocol)
TFTP – 69 – ( tftp port number )
Telnet – 23 – ( telnet port number)
SMTP – 25 – ( SMTP port number)
DNS – 53 – ( dns port number and Domain Name System port number)
DHCP – 68 – (DHCP port number and Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol port number )
POP3 – 110 – ( post office Protocol 3 port )
HTTP – 80 – (http port number)
HTTPS – 443 – (https port number)
NNTP – 119 – ( Network News Transfer Protocol Port number )
NTP – 123 – (ntp port number and network Time Protocol and SNTP port number )
IMAP – 143 – (Internet Message Access Protocol port number)
SSMTP – 465 – ( SMTP Over SSl )
SIMAP – 993 – ( IMAP Over SSL )
SPOP3 – 995 – ( POP# Over SS L)
Time – 123 – ( ntp port number and network Time Protocol and SNTP port number )
NetBios – 137 – ( Name Service )
NetBios – 139 – ( Datagram Service )
DHCP Client – 546 – (DHCP Client port number)
DHCP Server – 547 – (DHCP Server port number)
Global Catalog – 3268 – (Global Catalog port number)
LDAP – 389 – ( LDAP port number and Lightweight Directory Access Protocol port number )
RPC – 135 – (remote procedure call Port number)
Kerberos – 88 – ( Kerberos Port Number)
SSH – 22 – ( ssh port number and Secure Shell port number)
2. How to check tombstone lifetime value in your Forest
Tombstone lifetime value different from OS to OS, for windows server
2000/2003 it’s 60 days, In Windows Server 2003 SP1, default tombstone
lifetime (TSL) value has increased from 60 days to 180 days, again in
Windows Server 2003 R2 TSL value has been decreased to 60 days, Windows
Server 2003 R2 SP2 and windows server 2008 it’s 180 days
If you migrating windows 2003 environment to windows 2008 then its 60 day’s
If you migrating windows 2003 environment to windows 2008 then its 60 day’s
you can use the below command to check/view the current tombstone lifetime value for your Domain/Forest
dsquery * “cn=directory service,cn=windows nt,cn=services,cn=configuration,dc=” –scope base –attr tombstonelifetime
Replace forestDN with your domain partition DN, for domainname.com the DN would be dc=domainname, dc=com
3. How to find the domain controller that contains the lingering object
If we enable Strict Replication Consistency
Lingering objects are not present on domain controllers that log Event
ID 1988. The source domain controller contains the lingering object
If we doesn’t enable Strict Replication Consistency
Lingering objects are not present on domain controllers that log Event
ID 1388. Domain controller that doesn’t log Event ID 1388 and that
domain controller contain the lingering object
You have a 100 Domain controllers which doesn’t enable Strict
Replication Consistency, then you will get the Event ID 1388 on all the
99 Domain controllers except the one that contain the lingering object
Need to Remove Lingering Objects from the affected domain controller or decommission the domain controller
You can use Event Comb tool (Eventcombmt.exe)
is a multi-threaded tool that can be used to gather specific events
from the Event Viewer logs of different computers at the same time.
You can download these tools from the following location:
4. What are Active Directory ports:
List of Active Directory Ports for Active Directory replication and
Active Directory authentication, this ports can be used to configure the
Firewall
Active Directory replication- There is no defined port for Active Directory replication, Active Directory replication remote procedure calls (RPC) occur dynamically over an available port through RPCSS (RPC Endpoint Mapper) by using port 135
Active Directory replication- There is no defined port for Active Directory replication, Active Directory replication remote procedure calls (RPC) occur dynamically over an available port through RPCSS (RPC Endpoint Mapper) by using port 135
File Replication Services (FRS)- There is no defined
port for FRS, FRS replication over remote procedure calls (RPCs) occurs
dynamically over an available port by using RPCSS (RPC Endpoint Mapper )
on port 135
Other required ports for Active Directory
TCP 53 – DSN (DNS Download)
UDP 53 – DSN (DNS Queries)
TCP 42- WINS
UDP 42- WINS
TCP 3389- RDP (Remote Desktop)
TCP 135 – MS-RPC
TCP 1025 & 1026 – AD Login & replication
TCP 389 – LDAP
TCP 639 – LDAP over SSL/TLS
TCP 3268 -Global Catalog
TCP 3268 – Global Catalog over SSL/TSL
UDP 137 & 138 – NetBIOS related
UDP 88 – Kerberos v5
TCP 445 – SMB , Microsoft-ds
TCP 139 – SMB
TCP 53 – DSN (DNS Download)
UDP 53 – DSN (DNS Queries)
TCP 42- WINS
UDP 42- WINS
TCP 3389- RDP (Remote Desktop)
TCP 135 – MS-RPC
TCP 1025 & 1026 – AD Login & replication
TCP 389 – LDAP
TCP 639 – LDAP over SSL/TLS
TCP 3268 -Global Catalog
TCP 3268 – Global Catalog over SSL/TSL
UDP 137 & 138 – NetBIOS related
UDP 88 – Kerberos v5
TCP 445 – SMB , Microsoft-ds
TCP 139 – SMB
5. How to do active directory health checks?
As an administrator you have to check your active directory health daily
to reduce the active directory related issues, if you are not
monitoring the health of your active directory what will happen
Let’s say one of the Domain Controller failed to replicate, first day
you will not have any issue. If this will continue then you will have
login issue and you will not find the object change and new object,
that’s created and changed in other Domain Controller this will lead to
other issues
If the Domain Controller is not replicated more then 60 day’s then it will lead to Lingering issue
Command to check the replication to all the DC’s(through this we can check Active Directory Health)
Repadmin /replsum /bysrc /bydest /sort:delta
You can also save the command output to text file, by using the below command
Repadmin /replsum /bysrc /bydest /sort:delta >>c:\replication_report.txt
this will list the domain controllers that are failing to replicate with the delta value
You can daily run this to check your active directory health
You can daily run this to check your active directory health
6. GPRESULT falied with access denied error:
Unable to get the result from gpresult on windows 2003 server, gpresult
return with the access denied errors, you can able to update the group
policy without issue
Run the following commands to register the userenv.dll and recompile the rsop mof file
To resolve the access denied error while doing the gpresult.
1. Open a cmd
1. re-register the userenv.dll
Regsvr32 /n /I c:\winnt\system32\userenv.dll
2. CD c:\windows\system32\wbem
3. Mofcomp scersop.mof
4. Gpupdate /force
5. Gpresult
To resolve the access denied error while doing the gpresult.
1. Open a cmd
1. re-register the userenv.dll
Regsvr32 /n /I c:\winnt\system32\userenv.dll
2. CD c:\windows\system32\wbem
3. Mofcomp scersop.mof
4. Gpupdate /force
5. Gpresult
Now you able to run the gpresult without error and even server reboot not required for this procedure
7. What is the command to find out site name for given DC
dsquery server NYDC01 -site
domain controller name = NYDC01
8. Command to find all DCs in the given site
Command to find all the Domain Controllers in the “Default-First-Site-Name” site
dsquery server -o rdn -site Default-First-Site-Name
Site name = Default-First-Site-Name
9. How many types of queries DNS does?
Iterative Query
Recursive Query
Recursive Query
Iterative Query
In this query the client ask the name server for the best possible
answer, the name server check the cache and zone for which it’s
authoritative and returns the best possible answer to the client, which
would be the full answer like IP address or try the other name server
Recursive Query
Client demands either a full answer or an error message (like record or domain name does not exist)
Client machine always send recursive query to the DNS server, if the DNS server does not have the requested information, DNS server send the iterative query to the other name server (through forwarders or secondary DNS server) until it gets the information, or until the name query fails.
Client machine always send recursive query to the DNS server, if the DNS server does not have the requested information, DNS server send the iterative query to the other name server (through forwarders or secondary DNS server) until it gets the information, or until the name query fails.










No comments:
Post a Comment